Who wrote the Australian Constitution?
Thanks for your question Kirah and Kate!
The Australian Constitution was written by representatives from the colonial parliaments of New South Wales, Victoria, Queensland, South Australia, Western Australia and Tasmania at a series of meetings (called conventions) held in the 1880s and 1890s. Before Federation in 1901, Australia did not exist as a nation but was a collection of 6 British colonies. When the colonies agreed to unite (or federate) to form the Commonwealth of Australia, they needed a set of rules – a constitution – for how the new nation should work.
The representatives from the colonial parliaments included:
- Edmund Barton (NSW), who later became Australia’s first Prime Minister
- Henry Parkes (NSW)
- Alfred Deakin (Vic)
- Isaac Isaacs (Vic)
- Samuel Griffith (Qld)
- Charles Kingston (SA)
- John Forrest from (WA)
- Andrew Inglis Clarke (Tas).
The writers took some ideas from the Westminster system in the United Kingdom and from the Constitution of the United States of America. A referendum – a vote of the people – was then held in each colony between June 1899 and July 1900 to approve the Constitution.
Members of the Australasian Federation Conference, 1890
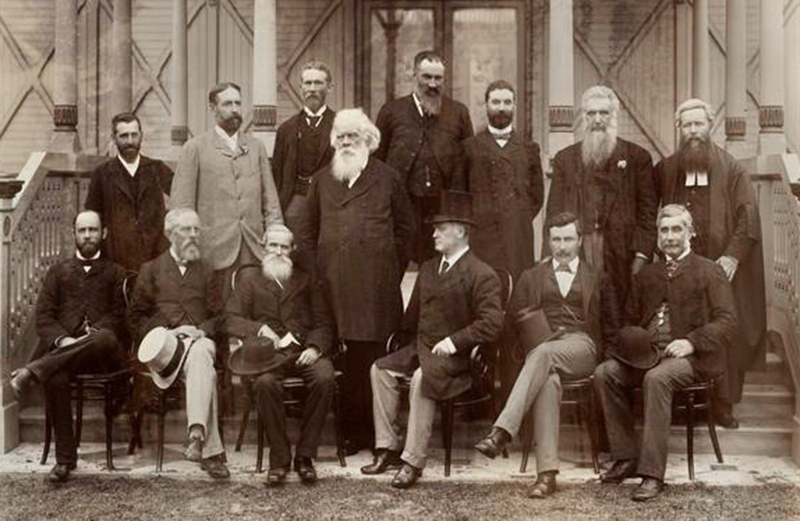
National Library of Australia, AN14292110
Description
This sepia-toned photo was taken at the Australasian Federation Conference in Melbourne in 1890. These 14 men were delegates from the 6 Australian colonies and the colony of New Zealand. At the Conference, they discussed the idea that the colonies should unite. Notable advocate for Federation Henry Parkes is standing fourth from left, and Alfred Deakin (who would go on to become Prime Minister of Australia) is standing sixth from left.
You may save or print this image for research and study. If you wish to use it for any other purposes, you must declare your Intention to Publish.