What’s the difference between a territory and a state parliament?
Thanks Fatna for your question. The main difference between state and territory parliaments is where they get their powers to make laws.
Each state has their own constitution which lists the powers of that state’s parliament, including the ability to make laws. The territories do not have their own constitutions. Section 122 of the Australian Constitution gives the Australian Parliament the power to make laws for territories. The Australian Parliament passed laws that give the ACT and Northern Territory Legislative Assemblies the power to make laws. The Australian Parliament can override a territory law but this is rare.
The Australian Capital Territory is unique in Australia because its parliament combines the responsibilities of both a local and state government.
Three levels of government in Australia
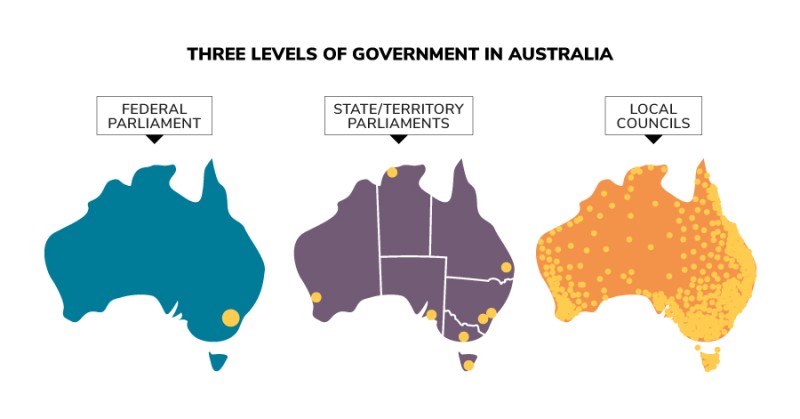
Parliamentary Education Office (peo.gov.au)
Description
The three levels of government – the law-making bodies in Australia. The Federal Parliament is located in Canberra, the nation's capital. State/territory parliaments are located in the capital cities of each of the 6 states and 2 territories. Local councils are located around Australia in each local council division.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License.
You are free to share – to copy, distribute and transmit the work.
Attribution – you must attribute the work in the manner specified by the author or licensor (but not in any way that suggests that they endorse you or your use of the work).
Non-commercial – you may not use this work for commercial purposes.
No derivative works – you may not alter, transform, or build upon this work.
Waiver – any of the above conditions can be waived if you get permission from the copyright holder.
