What are the different responsibilities between the State and Commonwealth governments when it comes to health care?
Thanks for your question.
Health care is a shared responsibility in Australia, meaning that both the federal and state/territory governments are able to make laws about it.
The way that health care is managed by both the federal and state/territory governments has developed over time, and continues to be negotiated between federal and state/territory governments. Generally, the federal government gives money to the states and territories for health services, as well as providing broad national policies on some health issues. The states and territories are more involved in the delivery of health services, such as the management of hospitals, doctors, nurses and other health care workers.
If you want more information about the areas of health care that federal and state governments are responsible for, you might like to visit their websites and compare their roles and powers.
Three levels of government in Australia
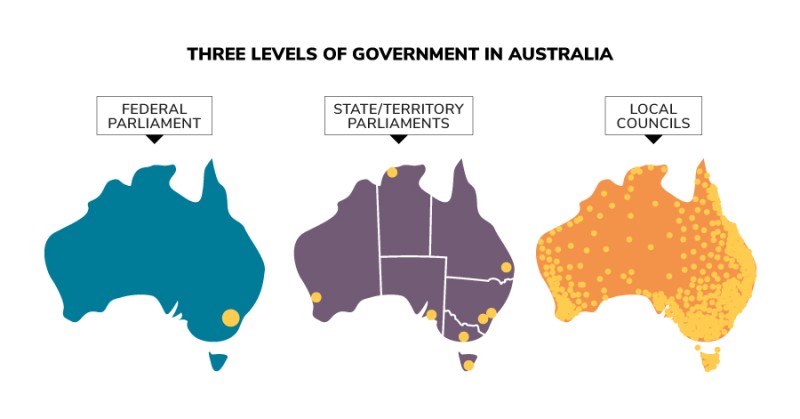
Parliamentary Education Office (peo.gov.au)
Description
The three levels of government – the law-making bodies in Australia. The Federal Parliament is located in Canberra, the nation's capital. State/territory parliaments are located in the capital cities of each of the 6 states and 2 territories. Local councils are located around Australia in each local council division.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License.
You are free to share – to copy, distribute and transmit the work.
Attribution – you must attribute the work in the manner specified by the author or licensor (but not in any way that suggests that they endorse you or your use of the work).
Non-commercial – you may not use this work for commercial purposes.
No derivative works – you may not alter, transform, or build upon this work.
Waiver – any of the above conditions can be waived if you get permission from the copyright holder.
