Under the Constitution is quarantine an Australian Government power?
Three levels of government in Australia
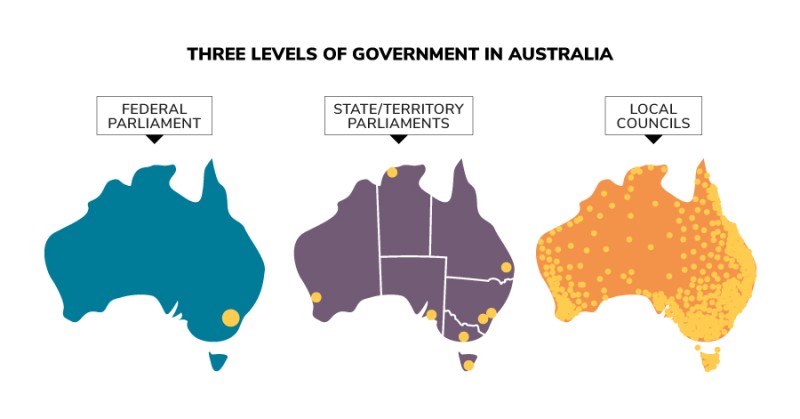
Parliamentary Education Office (peo.gov.au)
Description
The three levels of government – the law-making bodies in Australia. The Federal Parliament is located in Canberra, the nation's capital. State/territory parliaments are located in the capital cities of each of the 6 states and 2 territories. Local councils are located around Australia in each local council division.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License.
You are free to share – to copy, distribute and transmit the work.
Attribution – you must attribute the work in the manner specified by the author or licensor (but not in any way that suggests that they endorse you or your use of the work).
Non-commercial – you may not use this work for commercial purposes.
No derivative works – you may not alter, transform, or build upon this work.
Waiver – any of the above conditions can be waived if you get permission from the copyright holder.
Thank you for your question. The federal, state and territory governments work together to keep Australians safe by providing quarantine at our international borders and within Australia during public health emergencies.
Section 51(ix) of the Australian Constitution gives the Australian Parliament the exclusive – sole – power over quarantine as it relates to the movement of people, animals and goods in and out of Australia. This power is related to the external affairs power (section 51(xxix)).
The states and territories also have powers to quarantine people within their state or territory. They can do this as part of their powers to manage public health and deal with emergencies.
