How is a law/legislation removed or repealed in Australia and what is the process?
There are many reasons why the Australian Parliament might agree to repeal – undo or remove – an existing law; the law might be outdated or the government might want to deal with an issue differently.
Repealing a law requires the same process as making a new law. A repeal bill – proposed law – must be debated and agreed to by both the Senate and House of Representatives before it is signed into law by the Governor-General. The repeal bill will say when it comes into force.
Some laws do not need to be repealed because they have an expiry date called a sunset clause. All delegated law made by ministers and government departments has an expiry date unless the Parliament decides to renew it.
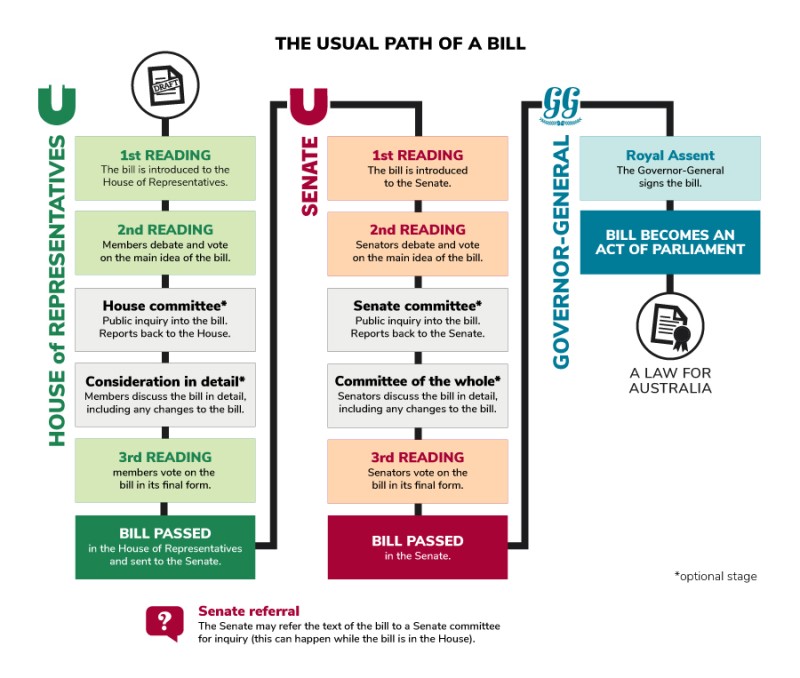
The usual path of a bill
Parliamentary Education Office (peo.gov.au)
Description
The usual path of a bill through the Australian Parliament to become Australian law.
In the House of Representatives a bill goes through the following stages:
- 1st reading – the bill is introduced to the House of Representatives
- 2nd reading – members debate and vote on the main idea of the bill
- House committee (optional stage) – public inquiry into the bill and reporting back to the House
- Consideration in detail (optional stage) – members discuss the bill in detail, including any changes to the bill
- 3rd reading – members vote on the bill in its final form
- the bill is passed in the House of Representatives and sent to the Senate.
Senate referral – the Senate may refer the text of the bill to a Senate committee for inquiry (this can happen while the bill is in the House).
In the Senate a bill goes through the following stages:
- 1st reading – the bill is introduced to the Senate
- 2nd reading – senators debate and vote on the main idea of the bill
- Senate committee (optional stage) – public inquiry into the bill and reporting back to the Senate
- Committee of the whole (optional stage) – senators discuss the bill in detail, including any changes to the bill
- 3rd reading – senators vote on the bill in its final form
- the bill is passed in the Senate.
The bill is given Royal Assent – The Governor-General signs the bill.
The bill becomes an Act of Parliament – a law for Australia.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License.
You are free to share – to copy, distribute and transmit the work.
Attribution – you must attribute the work in the manner specified by the author or licensor (but not in any way that suggests that they endorse you or your use of the work).
Non-commercial – you may not use this work for commercial purposes.
No derivative works – you may not alter, transform, or build upon this work.
Waiver – any of the above conditions can be waived if you get permission from the copyright holder.
