How did Australia become a democracy?
Many would say that the defining moment for Australian democracy was Federation in 1901.
Before 1901, Australia consisted of 6 British colonies which were partly self-governing but under the law-making power of the British Parliament. In the 1880s and 1890s, it was suggested the colonies might be stronger and more efficient if they worked together. Several conventions were held to draft an Australian Constitution. The Constitution was approved by a vote of the Australian people in referendums held in each colony between June 1899 and July 1900. It was then agreed to by the British Parliament. On 1 January 1901 the Australian colonies united to become a nation. This is known as federation and resulted in the creation of the Australian Parliament, with the colonies becoming Australia's 6 states. Through federation, the states transferred some of their law-making power to the Australian Parliament.
Australia is a representative democracy which means Australians elect members of parliament to make laws and decisions on our behalf.
Democracy key ideas
Parliamentary Education Office (peo.gov.au)
Description
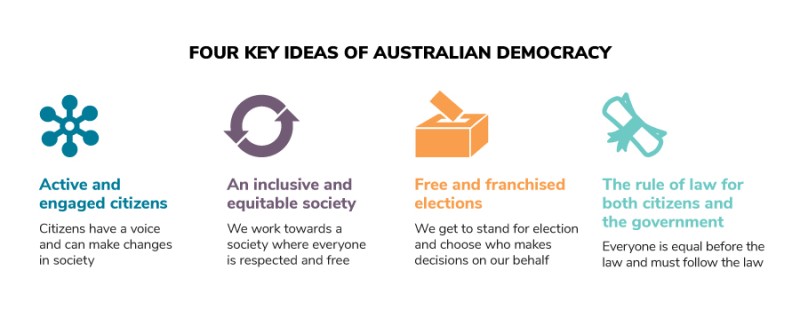
The 4 key ideas of Australian democracy are:
- Active and engaged citizens – Citizens have a voice and can make changes in society.
- An inclusive and equitable society – We work towards a society where everyone is respected and free.
- Free and franchised elections – We get to stand for election and choose who makes decision on our behalf.
- The rule of law for both citizens and the government – Everyone is equal before the law and must follow the law.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License.
You are free to share – to copy, distribute and transmit the work.
Attribution – you must attribute the work in the manner specified by the author or licensor (but not in any way that suggests that they endorse you or your use of the work).
Non-commercial – you may not use this work for commercial purposes.
No derivative works – you may not alter, transform, or build upon this work.
Waiver – any of the above conditions can be waived if you get permission from the copyright holder.
