Description
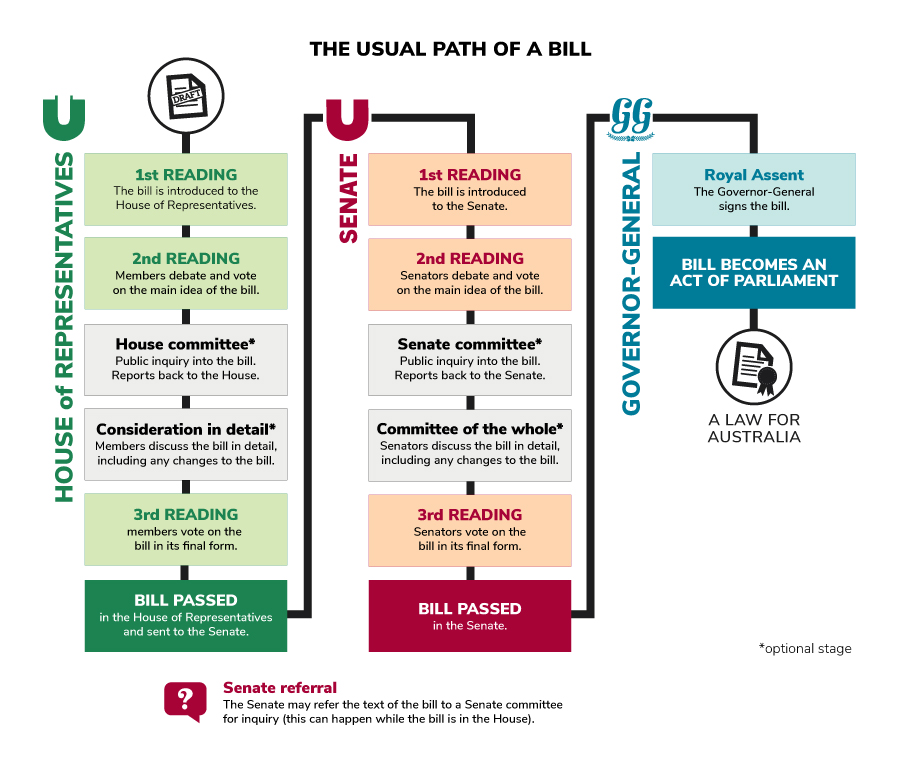
The usual path of a bill through the Australian Parliament to become Australian law.
In the House of Representatives a bill goes through the following stages:
- 1st reading – the bill is introduced to the House of Representatives
- 2nd reading – members debate and vote on the main idea of the bill
- House committee (optional stage) – public inquiry into the bill and reporting back to the House
- Consideration in detail (optional stage) – members discuss the bill in detail, including any changes to the bill
- 3rd reading – members vote on the bill in its final form
- the bill is passed in the House of Representatives and sent to the Senate.
Senate referral – the Senate may refer the text of the bill to a Senate committee for inquiry (this can happen while the bill is in the House).
In the Senate a bill goes through the following stages:
- 1st reading – the bill is introduced to the Senate
- 2nd reading – senators debate and vote on the main idea of the bill
- Senate committee (optional stage) – public inquiry into the bill and reporting back to the Senate
- Committee of the whole (optional stage) – senators discuss the bill in detail, including any changes to the bill
- 3rd reading – senators vote on the bill in its final form
- the bill is passed in the Senate.
The bill is given Royal Assent – The Governor-General signs the bill.
The bill becomes an Act of Parliament – a law for Australia.