Medicare starts
01 February 1984
Universal healthcare is established in Australia.
Medicare provides all Australians with access to free or subsidised medical and hospital care, regardless of their financial situation. When Medicare launched, over 14 million Australians – about 92% of the population – had registered for the program. Medicare reintroduced ‘bulk billing’ allowing people to visit doctors and public hospitals at no cost. Although there was opposition to Medicare upon its introduction, it is now enshrined in Australian life and is a major component of the Australian government’s budget.
The movement towards universal health care in Australia started in 1974 with the passing of the Health Insurance Bill 1973 in the joint sitting of Parliament. From 1976 Medibank delivered two strands of health coverage: Medibank Standard covered all Australians and was funded by a levy on people’s income – similar to Medicare; and Medibank Private was a private health insurance company. Medibank Standard was limited to low income earners in 1978 but was reintroduced for all Australians in a different form as Medicare in 1984.
The provision of payments for medical services was included in the Australian Constitution section 51 (xxiiiA)) after the social welfare referendum of 1946.
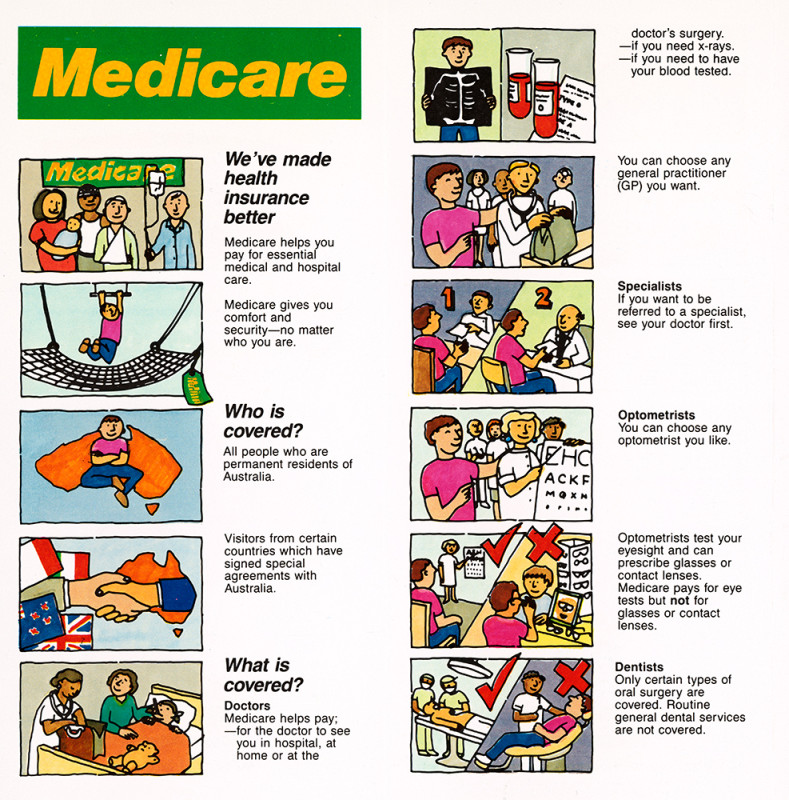
Medicare: ephemera material collected by the National Library of Australia
National Library of Australia, courtesy of Department of Human Services
Medicare: ephemera material collected by the National Library of Australia

National Library of Australia, courtesy of Department of Human Services
Description
This graphic from the 1980s was used to explain how Medicare worked for patients in Australia's healthcare system. Note: the information contained in this image is out-of-date and should not be relied upon.
You may save or print this image for research and study. If you wish to use it for any other purposes, you must declare your Intention to Publish.